Prerequisites
You always need a directory where you can write to with utl_file. And of course an ORACLE database.
The file extension has to be .xml, otherwise recent versions of Excel show a warning.
Differences Between Excel und OO-Calc
Some features are not available in Calc. These are shown in the tuorials.
Most Simple
The first step is to create a spreadsheet from a query.
DECLARE -- test_1.sql BEGIN xml_spreadsheet.abfrage( p_query => 'SELECT username, user_id, created ' || 'FROM all_users ' || 'WHERE UPPER(username) = ''HR'' ' ,p_path => 'DOC' ); END; /
That's it, not more code needed. The file name is set automatically to "query_<user>_<date>_<time>.xml", by default an autofilter is set for the heading row.
| Excel | OO-Calc |
|---|---|
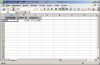 |
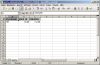 after renaming the generated filename to <...>.xml |
Click on images to enlarge |
|
The same result you'll get, when you pass a cursor.
DECLARE -- test_2.sql l_cursor number := dbms_sql.open_cursor; BEGIN dbms_sql.parse( l_cursor ,'SELECT username, user_id, created ' || 'FROM all_users ' || 'WHERE UPPER(username) = ''HR'' ' ,dbms_sql.native ); xml_spreadsheet.abfrage( p_cursor => l_cursor ,p_path => 'DOC' ); END; /
Set Headings and Summary Columns
Headings and summary columns are each just a list of VARCHAR2
DECLARE -- test_3.sql l_cursor number := dbms_sql.open_cursor; BEGIN dbms_sql.parse( l_cursor ,'SELECT employee_id,first_name,last_name,email,' || ' phone_number,hire_date,job_id,salary,' || ' commission_pct,manager_id,department_id ' || 'FROM employees ' ,dbms_sql.native ); xml_spreadsheet.abfrage( p_cursor => l_cursor ,p_path => 'DOC' ,p_sumColumns => xml_spreadsheet.t_tab_abfrage( 'N','N','N','N','N','N','N','Y','N','N','N') ,p_titles => xml_spreadsheet.t_tab_abfrage( 'Id','First Name','Last Name','Email','Phone Number', 'Hire Date','Job Id','Salary','Commission Pct', 'Manager Id','Department Id') ); END; /
| Excel | OO-Calc |
|---|---|
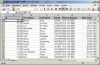 |
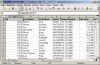 after renaming the generated filename to <...>.xml |
Click on images to enlarge |
|
This example works with passing a cursor or query string alike
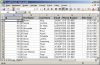
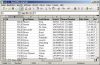
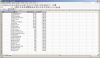
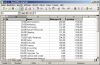
Add a Second Worksheet
When you have a list of your employees you might want to add a sheet with the associated departments.
In this case you need to remember the file handle, so you can add the second sheet to the correct file.
Also now a sheetname for each sheet is mandatory. The sheetname has to be unique within the file.
To add a third worksheet you would need to pass another parameter "p_close => FALSE", so the file is kept open.
DECLARE -- test_4.sql v_fileHandle utl_file.FILE_TYPE; BEGIN v_fileHandle := xml_spreadsheet.abfrage( p_query => 'SELECT employee_id,first_name,last_name,' || ' email,phone_number,hire_date,job_id,' || ' salary,commission_pct,manager_id,' || ' department_id ' || 'FROM employees ' ,p_path => 'DOC' ,p_filename => 'test_4.xml' ,p_sheetname => 'Emp' ,p_sumColumns => xml_spreadsheet.t_tab_abfrage( 'N','N','N','N','N','N','N','Y','N','N','N') ,p_titles => xml_spreadsheet.t_tab_abfrage( 'Id','First Name','Last Name','Email', 'Phone Number','Hire Date','Job Id','Salary', 'Commission Pct','Manager Id','Department Id') ,p_close => FALSE ); xml_spreadsheet.abfrage( p_query => 'SELECT department_id,department_name,' || ' manager_id,location_id ' || 'FROM departments ' ,p_fileHandle => v_fileHandle ,p_sheetname => 'Dept' ,p_titles => xml_spreadsheet.t_tab_abfrage( 'Id','Name','Manager Id','Location') ); END; /
| Excel | OO-Calc |
|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Click on images to enlarge |
|
This example works with passing a cursor or query string alike
Worksheet With Differently Formatted Numbers
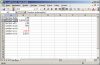
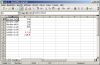
Instead of leaving the formatting of the data to the defaults of the package you can control the output. First we will use the predefined number formats.
Unlike befor we now have to take care when to open a file, worksheet or new row.
DECLARE -- test_5.sql v_fileHandle utl_file.FILE_TYPE; BEGIN -- New File v_fileHandle := xml_spreadsheet.createNewFile('DOC','test_5.xml'); -- open first worksheet xml_spreadsheet.newWorksheet( v_fileHandle ,'Numbers' ); -- Write a data row xml_spreadsheet.writeData(v_fileHandle,'Number Default'); xml_spreadsheet.writeData(v_fileHandle,100/39,xml_spreadsheet.c_numberDefault); -- New data row xml_spreadsheet.newDatarow(v_fileHandle); xml_spreadsheet.writeData(v_fileHandle,'Number unformatted'); xml_spreadsheet.writeData(v_fileHandle,100/39,xml_spreadsheet.c_unformatted); -- New data row xml_spreadsheet.newDatarow(v_fileHandle); xml_spreadsheet.writeData(v_fileHandle,'Number with two decimal digits'); xml_spreadsheet.writeData(v_fileHandle,100/39,xml_spreadsheet.c_number2decimal); -- New data row xml_spreadsheet.newDatarow(v_fileHandle); xml_spreadsheet.writeData(v_fileHandle,'number as percent'); xml_spreadsheet.writeData(v_fileHandle,39/100,xml_spreadsheet.c_prozent); -- New data row xml_spreadsheet.newDatarow(v_fileHandle); xml_spreadsheet.writeData(v_fileHandle,'number as integer'); xml_spreadsheet.writeData(v_fileHandle,100/39,xml_spreadsheet.c_integer); -- New data row xml_spreadsheet.newDatarow(v_fileHandle); xml_spreadsheet.writeData(v_fileHandle,'number as currency'); xml_spreadsheet.writeData(v_fileHandle,-100/39,xml_spreadsheet.c_currency); -- New data row xml_spreadsheet.newDatarow(v_fileHandle); xml_spreadsheet.writeData(v_fileHandle,'number as accounting format'); xml_spreadsheet.writeData(v_fileHandle,39/19,xml_spreadsheet.c_accounting); -- close worksheet xml_spreadsheet.closeWorksheet( v_fileHandle ,0 -- fix no rows in first worksheet when scrolling ); -- Close file xml_spreadsheet.closeFile(v_fileHandle); END; /
| Excel | OO-Calc |
|---|---|
 |
 |
Click on images to enlarge |
|
Differences
- Excel shows "unformatted" numbers with 8 decimal digits, OO-Calc with 2 decimal digits
- Excel shows "currency" correctly with EUR-sign (local default), OO-Calc uses USD-sign instead. Symbol is after value in Excel, before value in OO-Calc.
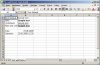
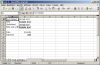
Worksheet With Differently Formatted Text And Date
Just like with the numbers you can control the output for text and date.
DECLARE -- test_6.sql v_fileHandle utl_file.FILE_TYPE; BEGIN -- New File v_fileHandle := xml_spreadsheet.createNewFile('DOC','test_6.xml'); -- open first worksheet xml_spreadsheet.newWorksheet( v_fileHandle ,'Text and Dates' ); -- Write a data row xml_spreadsheet.writeData(v_fileHandle,'Text Default'); xml_spreadsheet.writeData(v_fileHandle,'Sample text',xml_spreadsheet); -- New data row xml_spreadsheet.newDatarow(v_fileHandle); xml_spreadsheet.writeData(v_fileHandle,'Bold'); xml_spreadsheet.writeData(v_fileHandle,'Sample text',xml_spreadsheet.c_textBold); -- New data row xml_spreadsheet.newDatarow(v_fileHandle); xml_spreadsheet.writeData(v_fileHandle,'Underlined'); xml_spreadsheet.writeData(v_fileHandle,'Sample text',xml_spreadsheet.c_textUnderline); -- New data row xml_spreadsheet.newDatarow(v_fileHandle); xml_spreadsheet.writeData(v_fileHandle,'Bold and underlined'); xml_spreadsheet.writeData(v_fileHandle,'Sample text',xml_spreadsheet.c_textBoldUnderline); -- New data row xml_spreadsheet.newDatarow(v_fileHandle); xml_spreadsheet.newDatarow(v_fileHandle); xml_spreadsheet.writeData(v_fileHandle,'Date'); xml_spreadsheet.writeData(v_fileHandle,SYSDATE,xml_spreadsheet.c_date); -- New data row xml_spreadsheet.newDatarow(v_fileHandle); xml_spreadsheet.writeData(v_fileHandle,'Datetime'); xml_spreadsheet.writeData(v_fileHandle,-SYSDATE,xml_spreadsheet.c_dateTime); -- close worksheet xml_spreadsheet.closeWorksheet( v_fileHandle ,0 -- fix no rows in first worksheet when scrolling ); -- Close file xml_spreadsheet.closeFile(v_fileHandle); END; /
| Excel | OO-Calc |
|---|---|
 |
 |
Click on images to enlarge |
|
Differences
- Excel and OO-Calc show date and datetime with different formattings
- OO-Calc does not fit the column width for length of datetime